554 lines
21 KiB
Markdown
554 lines
21 KiB
Markdown
|
|
### Map 常用操作
|
|||
|
|
#### 初始化
|
|||
|
|
- var m1 map[string]int // m1 == nil 结果为true,此时写入会产生panic
|
|||
|
|
- var m2 = map[string]int{}
|
|||
|
|
- var m3 = make(map[string]int)
|
|||
|
|
- 函数类型、map 类型自身,以及切片类型是不能作为 map 的 key 类型的
|
|||
|
|
```go
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
s1 := make([]int, 1)
|
|||
|
|
s2 := make([]int, 2)
|
|||
|
|
f1 := func() {}
|
|||
|
|
f2 := func() {}
|
|||
|
|
m1 := make(map[int]string)
|
|||
|
|
m2 := make(map[int]string)
|
|||
|
|
println(s1 == s2) // 错误:invalid operation: s1 == s2 (slice can only be compared to nil)
|
|||
|
|
println(f1 == f2) // 错误:invalid operation: f1 == f2 (func can only be compared to nil)
|
|||
|
|
println(m1 == m2) // 错误:invalid operation: m1 == m2 (map can only be compared to nil)
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
- makemap_small 源码
|
|||
|
|
```go
|
|||
|
|
// makemap_small implements Go map creation for make(map[k]v) and
|
|||
|
|
// make(map[k]v, hint) when hint is known to be at most bucketCnt
|
|||
|
|
// at compile time and the map needs to be allocated on the heap.
|
|||
|
|
// 创建map不指定容量,或者容量小于bucketCnt(这个容量为8)
|
|||
|
|
func makemap_small() *hmap {
|
|||
|
|
h := new(hmap)
|
|||
|
|
h.hash0 = fastrand()
|
|||
|
|
return h
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
- makemap 源码
|
|||
|
|
```go
|
|||
|
|
// makemap implements Go map creation for make(map[k]v, hint).
|
|||
|
|
// If the compiler has determined that the map or the first bucket
|
|||
|
|
// can be created on the stack, h and/or bucket may be non-nil.
|
|||
|
|
// If h != nil, the map can be created directly in h.
|
|||
|
|
// If h.buckets != nil, bucket pointed to can be used as the first bucket.
|
|||
|
|
func makemap(t *maptype, hint int, h *hmap) *hmap {
|
|||
|
|
mem, overflow := math.MulUintptr(uintptr(hint), t.bucket.size)
|
|||
|
|
// 数据范围溢出,设置为0
|
|||
|
|
if overflow || mem > maxAlloc {
|
|||
|
|
hint = 0
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// initialize Hmap
|
|||
|
|
if h == nil {
|
|||
|
|
h = new(hmap)
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
// 随机种子
|
|||
|
|
h.hash0 = fastrand()
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// Find the size parameter B which will hold the requested # of elements.
|
|||
|
|
// For hint < 0 overLoadFactor returns false since hint < bucketCnt.
|
|||
|
|
B := uint8(0)
|
|||
|
|
for overLoadFactor(hint, B) {
|
|||
|
|
B++
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
h.B = B
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// allocate initial hash table
|
|||
|
|
// if B == 0, the buckets field is allocated lazily later (in mapassign)
|
|||
|
|
// If hint is large zeroing this memory could take a while.
|
|||
|
|
if h.B != 0 {
|
|||
|
|
var nextOverflow *bmap
|
|||
|
|
h.buckets, nextOverflow = makeBucketArray(t, h.B, nil)
|
|||
|
|
if nextOverflow != nil {
|
|||
|
|
h.extra = new(mapextra)
|
|||
|
|
h.extra.nextOverflow = nextOverflow
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
return h
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### 写map
|
|||
|
|
- key, value 写入
|
|||
|
|
- mapassign源码
|
|||
|
|
```go
|
|||
|
|
// Like mapaccess, but allocates a slot for the key if it is not present in the map.
|
|||
|
|
func mapassign(t *maptype, h *hmap, key unsafe.Pointer) unsafe.Pointer {
|
|||
|
|
if h == nil {
|
|||
|
|
panic(plainError("assignment to entry in nil map"))
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
if raceenabled {
|
|||
|
|
callerpc := getcallerpc()
|
|||
|
|
pc := funcPC(mapassign)
|
|||
|
|
racewritepc(unsafe.Pointer(h), callerpc, pc)
|
|||
|
|
raceReadObjectPC(t.key, key, callerpc, pc)
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
if msanenabled {
|
|||
|
|
msanread(key, t.key.size)
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
// hashWriting = 4 固定值 二进制 0000 0100
|
|||
|
|
if h.flags&hashWriting != 0 {
|
|||
|
|
throw("concurrent map writes")
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
hash := t.hasher(key, uintptr(h.hash0))
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// Set hashWriting after calling t.hasher, since t.hasher may panic,
|
|||
|
|
// in which case we have not actually done a write.
|
|||
|
|
// map真正写入前设置标记位,其他goroutine写入会马上 throw("concurrent map writes")
|
|||
|
|
// 异或操作,相同为0,不同为1,修改第三位为1,保留其他位为原值,再次进行与操作时,等于1,然后就会崩溃
|
|||
|
|
h.flags ^= hashWriting
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
if h.buckets == nil {
|
|||
|
|
h.buckets = newobject(t.bucket) // newarray(t.bucket, 1)
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// 省略部分代码
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### 读map
|
|||
|
|
- value := hash[key]
|
|||
|
|
- value, ok := hash[key]
|
|||
|
|
- 如果key不存在,返回value类型的零值
|
|||
|
|
- mapaccess1 返回val 源码
|
|||
|
|
- mapaccess2 返回val和bool
|
|||
|
|
```go
|
|||
|
|
// mapaccess1 returns a pointer to h[key]. Never returns nil, instead
|
|||
|
|
// it will return a reference to the zero object for the elem type if
|
|||
|
|
// the key is not in the map.
|
|||
|
|
// NOTE: The returned pointer may keep the whole map live, so don't
|
|||
|
|
// hold onto it for very long.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// key不存在返回类型的零值
|
|||
|
|
// 不要持有返回的指针太长时间,容易造成GC无法回收map,导致内存泄漏
|
|||
|
|
func mapaccess1(t *maptype, h *hmap, key unsafe.Pointer) unsafe.Pointer {
|
|||
|
|
if raceenabled && h != nil {
|
|||
|
|
callerpc := getcallerpc()
|
|||
|
|
pc := funcPC(mapaccess1)
|
|||
|
|
racereadpc(unsafe.Pointer(h), callerpc, pc)
|
|||
|
|
raceReadObjectPC(t.key, key, callerpc, pc)
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
if msanenabled && h != nil {
|
|||
|
|
msanread(key, t.key.size)
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
// map 为空
|
|||
|
|
if h == nil || h.count == 0 {
|
|||
|
|
if t.hashMightPanic() {
|
|||
|
|
t.hasher(key, 0) // see issue 23734
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
return unsafe.Pointer(&zeroVal[0])
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
// 有正在写的goroutine,崩溃fatal error
|
|||
|
|
if h.flags&hashWriting != 0 {
|
|||
|
|
throw("concurrent map read and map write")
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
hash := t.hasher(key, uintptr(h.hash0)) // 根据key计算的hash值
|
|||
|
|
m := bucketMask(h.B) // 桶的个数
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// 指针计算,找到key应该在的bmap
|
|||
|
|
b := (*bmap)(add(h.buckets, (hash&m)*uintptr(t.bucketsize)))
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// 桶正在扩容
|
|||
|
|
if c := h.oldbuckets; c != nil {
|
|||
|
|
if !h.sameSizeGrow() {
|
|||
|
|
// There used to be half as many buckets; mask down one more power of two.
|
|||
|
|
m >>= 1
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
oldb := (*bmap)(add(c, (hash&m)*uintptr(t.bucketsize)))
|
|||
|
|
if !evacuated(oldb) {
|
|||
|
|
b = oldb
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
top := tophash(hash)
|
|||
|
|
// 遍历bucket
|
|||
|
|
bucketloop:
|
|||
|
|
for ; b != nil; b = b.overflow(t) {
|
|||
|
|
for i := uintptr(0); i < bucketCnt; i++ {
|
|||
|
|
if b.tophash[i] != top {
|
|||
|
|
if b.tophash[i] == emptyRest {
|
|||
|
|
break bucketloop
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
continue
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
k := add(unsafe.Pointer(b), dataOffset+i*uintptr(t.keysize))
|
|||
|
|
if t.indirectkey() {
|
|||
|
|
k = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(k))
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
if t.key.equal(key, k) {
|
|||
|
|
e := add(unsafe.Pointer(b), dataOffset+bucketCnt*uintptr(t.keysize)+i*uintptr(t.elemsize))
|
|||
|
|
if t.indirectelem() {
|
|||
|
|
e = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(e))
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
return e
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
// 没有的话 返回零值
|
|||
|
|
return unsafe.Pointer(&zeroVal[0])
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### 删除map中的元素
|
|||
|
|
- delete(map, key)
|
|||
|
|
- `mapdelete` 方法
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### range map
|
|||
|
|
- 调用 `mapiterinit` 方法进行初始化
|
|||
|
|
- 不断调用 `mapiternext` 方法进行循环
|
|||
|
|
### 特性
|
|||
|
|
- map是个指针,底层指向hmap,所以是个引用类型
|
|||
|
|
- golang slice、map、channel都是引用类型,当引用类型作为函数参数时,可能会修改原内容数据
|
|||
|
|
- golang 中没有引用传递,只有值和指针传递。map 作为函数实参传递时本质上也是值传递,因为 map 底层数据结构是通过指针指向实际的元素存储空间,在被调函数中修改 map,对调用者同样可见,所以 map 作为函数实参传递时表现出了引用传递的效果
|
|||
|
|
- map 底层数据结构是通过指针指向实际的元素存储空间,对其中一个map的更改,会影响到其他map
|
|||
|
|
- 遍历无序
|
|||
|
|
- map 可以自动扩容,map 中数据元素的 value 位置可能在这一过程中发生变化,所以 Go 不允许获取 map 中 value 的地址,这个约束是在编译期间就生效的
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### Map 实现原理
|
|||
|
|
- Go中的map是一个指针,占用8个字节,指向hmap结构体; 源码src/runtime/map.go中可以看到map的底层结构
|
|||
|
|
- 每个map的底层结构是hmap,hmap包含若干个结构为bmap的bucket数组。每个bucket底层都采用链表结构
|
|||
|
|
- 每个 bucket 中存储的是 Hash 值低 bit 位数值相同的元素,默认的元素个数为 BUCKETSIZE(值为 8,Go 1.17 版本中在 $GOROOT/src/cmd/compile/internal/reflectdata/reflect.go 中定义,与runtime/map.go 中常量 bucketCnt 保持一致)
|
|||
|
|
- 当某个 bucket(比如 buckets[0]) 的 8 个空槽 slot)都填满了,且 map 尚未达到扩容的条件的情况下,运行时会建立 overflow bucket,并将这个 overflow bucket 挂在上面 bucket(如 buckets[0])末尾的 overflow 指针上,这样两个 buckets 形成了一个链表结构,直到下一次 map 扩容之前,这个结构都会一直存在
|
|||
|
|
- map 结构,key和value单独排列在一起可以减少结构体对齐填充,减少内存浪费
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
```golang
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// A header for a Go map.
|
|||
|
|
type hmap struct {
|
|||
|
|
count int
|
|||
|
|
// 代表哈希表中的元素个数,调用len(map)时,返回的就是该字段值。
|
|||
|
|
flags uint8 // 标记 扩容状态,读写状态
|
|||
|
|
B uint8
|
|||
|
|
// buckets(桶)的对数log_2
|
|||
|
|
// 如果B=5,则buckets数组的长度 = 2^5=32,意味着有32个桶
|
|||
|
|
noverflow uint16
|
|||
|
|
// 溢出桶的大概数量
|
|||
|
|
hash0 uint32
|
|||
|
|
// 哈希种子
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
buckets unsafe.Pointer
|
|||
|
|
// 指向buckets数组的指针,数组大小为2^B,如果元素个数为0,它为nil。
|
|||
|
|
oldbuckets unsafe.Pointer
|
|||
|
|
// 如果发生扩容,oldbuckets是指向老的buckets数组的指针,
|
|||
|
|
// 老的buckets数组大小是新的buckets的1/2;非扩容状态下,它为nil。
|
|||
|
|
nevacuate uintptr
|
|||
|
|
// 表示扩容进度,小于此地址的buckets代表已搬迁完成。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
extra *mapextra
|
|||
|
|
// 这个字段是为了优化GC扫描而设计的。当key和value均不包含指针
|
|||
|
|
// 并且都可以inline时使用。extra是指向mapextra类型的指针。
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
- bmap结构
|
|||
|
|
```go
|
|||
|
|
bucketCntBits = 3
|
|||
|
|
bucketCnt = 1 << bucketCntBits
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// A bucket for a Go map.
|
|||
|
|
type bmap struct {
|
|||
|
|
// tophash generally contains the top byte of the hash value
|
|||
|
|
// for each key in this bucket. If tophash[0] < minTopHash,
|
|||
|
|
// tophash[0] is a bucket evacuation state instead.
|
|||
|
|
tophash [bucketCnt]uint8
|
|||
|
|
// Followed by bucketCnt keys and then bucketCnt elems.
|
|||
|
|
// NOTE: packing all the keys together and then all the elems together makes the
|
|||
|
|
// code a bit more complicated than alternating key/elem/key/elem/... but it allows
|
|||
|
|
// us to eliminate padding which would be needed for, e.g., map[int64]int8.
|
|||
|
|
// Followed by an overflow pointer.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// len为8的数组
|
|||
|
|
// 用来快速定位key是否在这个bmap中
|
|||
|
|
// 桶的槽位数组,一个桶最多8个槽位,如果key所在的槽位在tophash中,则代表该key在这个桶中
|
|||
|
|
// key 单独放在一起,value单独放在一起,相同的类型放在一起,减少空间浪费,
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
- mapextra结构
|
|||
|
|
```go
|
|||
|
|
// mapextra holds fields that are not present on all maps.
|
|||
|
|
// 字面理解附加字段
|
|||
|
|
type mapextra struct {
|
|||
|
|
// If both key and elem do not contain pointers and are inline, then we mark bucket
|
|||
|
|
// type as containing no pointers. This avoids scanning such maps.
|
|||
|
|
// However, bmap.overflow is a pointer. In order to keep overflow buckets
|
|||
|
|
// alive, we store pointers to all overflow buckets in hmap.extra.overflow and hmap.extra.oldoverflow.
|
|||
|
|
// overflow and oldoverflow are only used if key and elem do not contain pointers.
|
|||
|
|
// overflow contains overflow buckets for hmap.buckets.
|
|||
|
|
// oldoverflow contains overflow buckets for hmap.oldbuckets.
|
|||
|
|
// The indirection allows to store a pointer to the slice in hiter.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// 如果 key 和 value 都不包含指针,并且可以被 inline(<=128 字节)
|
|||
|
|
// 就使用 hmap的extra字段 来存储 overflow buckets,这样可以避免 GC 扫描整个 map
|
|||
|
|
// 然而 bmap.overflow 也是个指针。这时候我们只能把这些 overflow 的指针
|
|||
|
|
// 都放在 hmap.extra.overflow 和 hmap.extra.oldoverflow 中了
|
|||
|
|
// overflow 包含的是 hmap.buckets 的 overflow 的 buckets
|
|||
|
|
// oldoverflow 包含扩容时的 hmap.oldbuckets 的 overflow 的 bucket
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
overflow *[]*bmap
|
|||
|
|
oldoverflow *[]*bmap
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// nextOverflow holds a pointer to a free overflow bucket.
|
|||
|
|
nextOverflow *bmap
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### tophash区域
|
|||
|
|
- 向 map 插入一条数据,或者是从 map 按 key 查询数据的时候,运行时都会使用哈希函数对 key 做哈希运算,并获得一个哈希值(hashcode)
|
|||
|
|
- 运行时会把 hashcode“一分为二”来看待,其中低位区的值用于选定 bucket,高位区的值用于在某个 bucket 中确定 key 的位置
|
|||
|
|
- 每个 bucket 的 tophash 区域其实是用来快速定位 key 位置的,避免了逐个 key 进行比较这种代价较大的操作
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 为什么遍历map无序?
|
|||
|
|
- range map,初始化时调用`fastrand()`随机一个数字,决定本次range的起始点
|
|||
|
|
```go
|
|||
|
|
// mapiterinit initializes the hiter struct used for ranging over maps.
|
|||
|
|
// The hiter struct pointed to by 'it' is allocated on the stack
|
|||
|
|
// by the compilers order pass or on the heap by reflect_mapiterinit.
|
|||
|
|
// Both need to have zeroed hiter since the struct contains pointers.
|
|||
|
|
func mapiterinit(t *maptype, h *hmap, it *hiter) {
|
|||
|
|
// 省略一部分
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// decide where to start
|
|||
|
|
// 开始迭代时会有一个随机数,决定起始位置
|
|||
|
|
r := uintptr(fastrand())
|
|||
|
|
if h.B > 31-bucketCntBits {
|
|||
|
|
r += uintptr(fastrand()) << 31
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
it.startBucket = r & bucketMask(h.B)
|
|||
|
|
it.offset = uint8(r >> h.B & (bucketCnt - 1))
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// iterator state
|
|||
|
|
it.bucket = it.startBucket
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// Remember we have an iterator.
|
|||
|
|
// Can run concurrently with another mapiterinit().
|
|||
|
|
if old := h.flags; old&(iterator|oldIterator) != iterator|oldIterator {
|
|||
|
|
atomic.Or8(&h.flags, iterator|oldIterator)
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
mapiternext(it)
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 怎么有序遍历map
|
|||
|
|
- 先取出map的key
|
|||
|
|
- 对key进行排序
|
|||
|
|
- 循环排序后的key,实现有序遍历map
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 为什么map非线程安全
|
|||
|
|
- 并发访问需要控制锁相关,防止出现资源竞争
|
|||
|
|
- 大部分不需要从多个goroutine同时读写map,加锁反而造成性能降低
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```go
|
|||
|
|
func mapiternext(it *hiter) {
|
|||
|
|
h := it.h
|
|||
|
|
if raceenabled {
|
|||
|
|
callerpc := getcallerpc()
|
|||
|
|
racereadpc(unsafe.Pointer(h), callerpc, funcPC(mapiternext))
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
if h.flags&hashWriting != 0 {
|
|||
|
|
// 直接抛出异常,fatal error
|
|||
|
|
throw("concurrent map iteration and map write")
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
t := it.t
|
|||
|
|
bucket := it.bucket
|
|||
|
|
b := it.bptr
|
|||
|
|
i := it.i
|
|||
|
|
checkBucket := it.checkBucket
|
|||
|
|
// 省略部分代码
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 线程安全的map怎么实现
|
|||
|
|
- 使用读写锁 `map` + `sync.RWMutex`
|
|||
|
|
- [sync.Map](../../mkdocs_wiki/go/sync_map.md)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### map扩容策略
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 装载因子超过阈值,源码里定义的阈值是 6.5
|
|||
|
|
- overflow 的 bucket 数量过多:当 B 小于 15,也即 bucket 总数小于 2^15 时,overflow 的 bucket 数量超过 2^B;当 B >= 15,也即 bucket 总数大于等于 2^15时,overflow 的 bucket 数量超过 2^15。
|
|||
|
|
- 命中装载因子增量扩容
|
|||
|
|
- 命中溢出桶太多,等量扩容
|
|||
|
|
- 扩容时,只是把原来的桶挂载到新的桶上,然后采用增量复制去迁移桶内的数据
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```go
|
|||
|
|
// Maximum average load of a bucket that triggers growth is 6.5.
|
|||
|
|
// Represent as loadFactorNum/loadFactorDen, to allow integer math.
|
|||
|
|
loadFactorNum = 13
|
|||
|
|
loadFactorDen = 2
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// growing reports whether h is growing. The growth may be to the same size or bigger.
|
|||
|
|
func (h *hmap) growing() bool {
|
|||
|
|
return h.oldbuckets != nil
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// overLoadFactor reports whether count items placed in 1<<B buckets is over loadFactor.
|
|||
|
|
func overLoadFactor(count int, B uint8) bool {
|
|||
|
|
return count > bucketCnt && uintptr(count) > loadFactorNum*(bucketShift(B)/loadFactorDen)
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// tooManyOverflowBuckets reports whether noverflow buckets is too many for a map with 1<<B buckets.
|
|||
|
|
// Note that most of these overflow buckets must be in sparse use;
|
|||
|
|
// if use was dense, then we'd have already triggered regular map growth.
|
|||
|
|
func tooManyOverflowBuckets(noverflow uint16, B uint8) bool {
|
|||
|
|
// If the threshold is too low, we do extraneous work.
|
|||
|
|
// If the threshold is too high, maps that grow and shrink can hold on to lots of unused memory.
|
|||
|
|
// "too many" means (approximately) as many overflow buckets as regular buckets.
|
|||
|
|
// See incrnoverflow for more details.
|
|||
|
|
if B > 15 {
|
|||
|
|
B = 15
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
// 15 & 15 = 15
|
|||
|
|
// 判断符右边最大的结果就是1 << 15
|
|||
|
|
// 这个操作可能是见的太少,为什么要用15呢?
|
|||
|
|
// The compiler doesn't see here that B < 16; mask B to generate shorter shift code.
|
|||
|
|
return noverflow >= uint16(1)<<(B&15)
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// Did not find mapping for key. Allocate new cell & add entry.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// If we hit the max load factor or we have too many overflow buckets,
|
|||
|
|
// and we're not already in the middle of growing, start growing.
|
|||
|
|
// 最大装载因子或者溢出桶太多,然后还没有在扩容状态,开始扩容
|
|||
|
|
if !h.growing() && (overLoadFactor(h.count+1, h.B) || tooManyOverflowBuckets(h.noverflow, h.B)) {
|
|||
|
|
hashGrow(t, h)
|
|||
|
|
goto again
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
func hashGrow(t *maptype, h *hmap) {
|
|||
|
|
// 命中装载因子,增量扩容
|
|||
|
|
// 溢出桶太多,等量扩容
|
|||
|
|
// If we've hit the load factor, get bigger.
|
|||
|
|
// Otherwise, there are too many overflow buckets,
|
|||
|
|
// so keep the same number of buckets and "grow" laterally.
|
|||
|
|
bigger := uint8(1)
|
|||
|
|
if !overLoadFactor(h.count+1, h.B) {
|
|||
|
|
bigger = 0
|
|||
|
|
h.flags |= sameSizeGrow
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
oldbuckets := h.buckets
|
|||
|
|
newbuckets, nextOverflow := makeBucketArray(t, h.B+bigger, nil)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
flags := h.flags &^ (iterator | oldIterator)
|
|||
|
|
if h.flags&iterator != 0 {
|
|||
|
|
flags |= oldIterator
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
// commit the grow (atomic wrt gc)
|
|||
|
|
h.B += bigger // 如果bigger是0就是等量扩容,是1就是2倍,翻倍扩容
|
|||
|
|
h.flags = flags
|
|||
|
|
h.oldbuckets = oldbuckets
|
|||
|
|
h.buckets = newbuckets
|
|||
|
|
h.nevacuate = 0
|
|||
|
|
h.noverflow = 0
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
if h.extra != nil && h.extra.overflow != nil {
|
|||
|
|
// Promote current overflow buckets to the old generation.
|
|||
|
|
if h.extra.oldoverflow != nil {
|
|||
|
|
throw("oldoverflow is not nil")
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
h.extra.oldoverflow = h.extra.overflow
|
|||
|
|
h.extra.overflow = nil
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
if nextOverflow != nil {
|
|||
|
|
if h.extra == nil {
|
|||
|
|
h.extra = new(mapextra)
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
h.extra.nextOverflow = nextOverflow
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// 哈希表数据的实际复制是增量完成的
|
|||
|
|
// 通过growWork() 和evacuate()。
|
|||
|
|
// the actual copying of the hash table data is done incrementally
|
|||
|
|
// by growWork() and evacuate().
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// 写或者删map中的元素才会调用growWork
|
|||
|
|
// mapassign
|
|||
|
|
// mapdelete
|
|||
|
|
func growWork(t *maptype, h *hmap, bucket uintptr) {
|
|||
|
|
// make sure we evacuate the oldbucket corresponding
|
|||
|
|
// to the bucket we're about to use
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
evacuate(t, h, bucket&h.oldbucketmask())
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// evacuate one more oldbucket to make progress on growing
|
|||
|
|
if h.growing() {
|
|||
|
|
evacuate(t, h, h.nevacuate)
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// 迁移桶内数据
|
|||
|
|
func evacuate(t *maptype, h *hmap, oldbucket uintptr) {
|
|||
|
|
b := (*bmap)(add(h.oldbuckets, oldbucket*uintptr(t.bucketsize)))
|
|||
|
|
newbit := h.noldbuckets()
|
|||
|
|
if !evacuated(b) {
|
|||
|
|
// TODO: reuse overflow buckets instead of using new ones, if there
|
|||
|
|
// is no iterator using the old buckets. (If !oldIterator.)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// 先搞长度2个的数组
|
|||
|
|
// xy contains the x and y (low and high) evacuation destinations.
|
|||
|
|
var xy [2]evacDst
|
|||
|
|
x := &xy[0] // 用一个
|
|||
|
|
x.b = (*bmap)(add(h.buckets, oldbucket*uintptr(t.bucketsize)))
|
|||
|
|
x.k = add(unsafe.Pointer(x.b), dataOffset)
|
|||
|
|
x.e = add(x.k, bucketCnt*uintptr(t.keysize))
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
if !h.sameSizeGrow() { // 不是等量扩容,再用另一个
|
|||
|
|
// Only calculate y pointers if we're growing bigger.
|
|||
|
|
// Otherwise GC can see bad pointers.
|
|||
|
|
y := &xy[1]
|
|||
|
|
y.b = (*bmap)(add(h.buckets, (oldbucket+newbit)*uintptr(t.bucketsize)))
|
|||
|
|
y.k = add(unsafe.Pointer(y.b), dataOffset)
|
|||
|
|
y.e = add(y.k, bucketCnt*uintptr(t.keysize))
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### map哈希冲突解决方法
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 开放寻址法:**依次探测和比较数组中的元素以判断目标键值对是否存在于哈希表中**,使用开放寻址法来实现哈希表,那么实现哈希表底层的数据结构就是数组
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 首次索引写入位置 `index := hash("author") % array.len`
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 如果发生冲突,就会将键值对写入到下一个索引不为空的位置
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
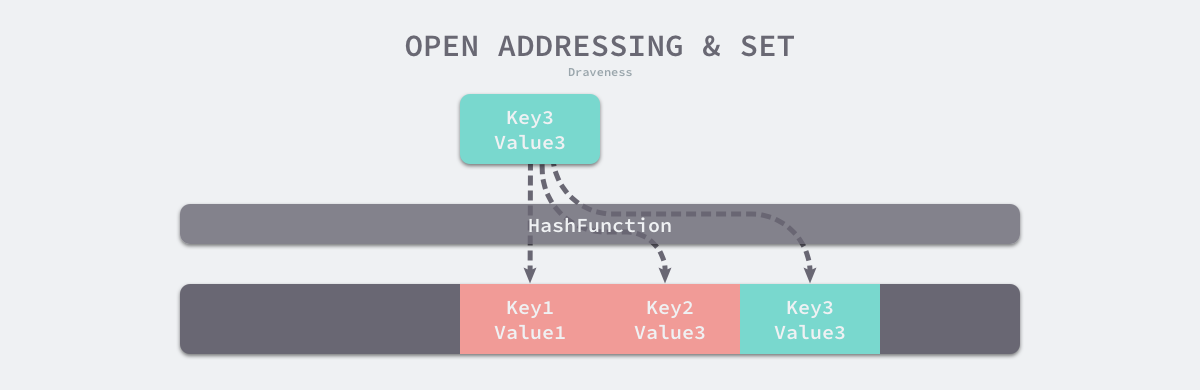
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 读取数据时,会从index位置开始读取并判断key是否相等,不相等的话读下一个索引位置,直到读到或者key为空时返回数据
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
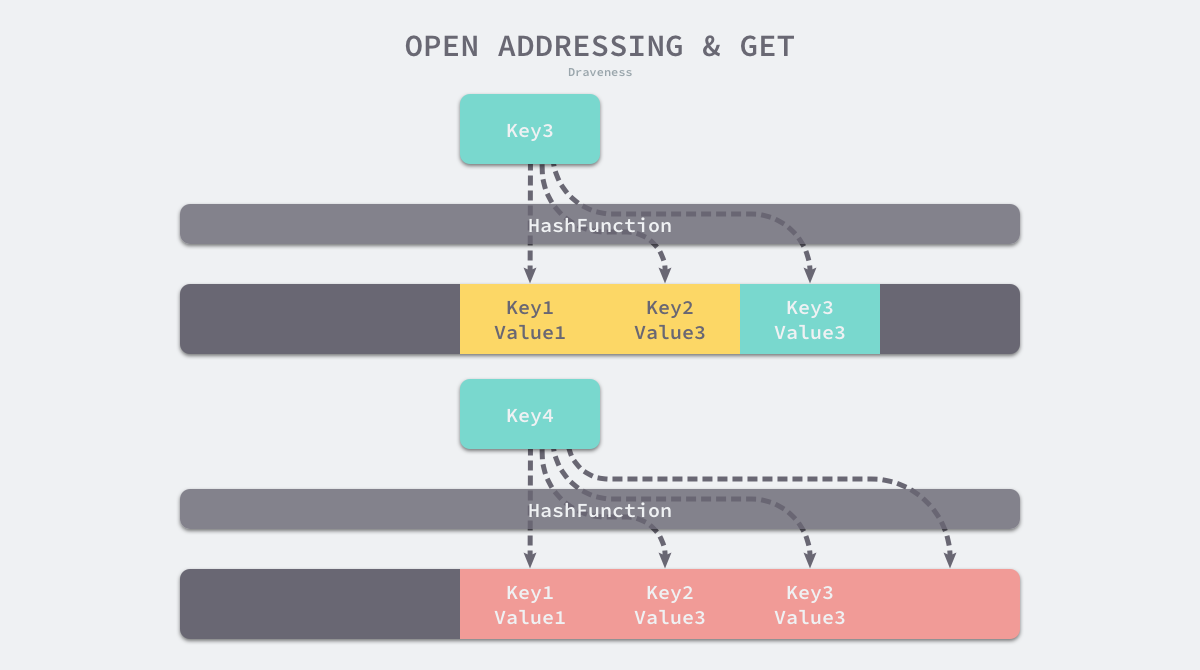
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 装载因子:数组中元素与数组长度的比值,随着装载因子的增加,线性探测的平均用时就会逐渐增加,会影响哈希表的读写性能。当装载率超过 70% 之后,哈希表的性能就会急剧下降,而一旦装载率达到 100%,整个哈希表就会完全失效,这时查找和插入任意元素的时间复杂度都是 𝑂(𝑛) 的,这时需要遍历数组中的全部元素
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 拉链法
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 一般会使用数组加上链表,一些编程语言会在拉链法的哈希中引入红黑树以优化性能,拉链法会使用链表数组作为哈希底层的数据结构,可以将它看成可以扩展的二维数组:
|
|||
|
|
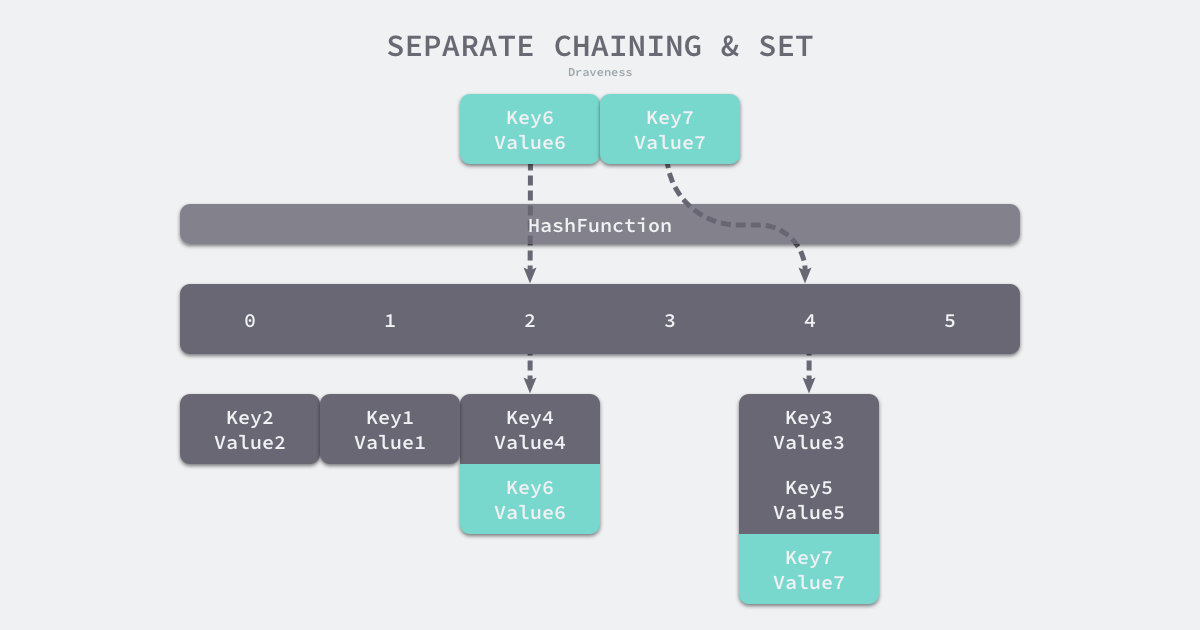
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 数组索引位置计算 `index := hash("Key6") % array.len`,根据索引位置,就可以遍历当前桶中的链表,在遍历链表的过程中会遇到以下两种情况:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
1. 找到键相同的键值对 — 更新键对应的值;
|
|||
|
|
2. 没有找到键相同的键值对 — 在链表的末尾追加新的键值对
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 装载因子:=元素数量÷桶数量
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|